A static IP address can be very useful in some cases, and can even improve your security. If you want to set up a local server or improve your internet speeds, configuring a static IP address on different devices is a very simple process. In this article, we’ll guide you through the steps so you can have a working static IP address in no time.
Note: ExpressVPN offers dynamic IPs by default, which change each time you connect, enhancing your privacy. For users who need a consistent IP address, ExpressVPN also provides a dedicated IP option. If you specifically need a static IP directly from your ISP, here’s how to set one up.
What is a static IP?
An IP address is a unique series of numbers that identifies each device on a local network or the internet. An IP address can be dynamic or static.
Most people use dynamic IP addresses, which change automatically and regularly—most commonly every 24 hours or after a router reset. This means when you go online, your IP address should be different from the one you had the day before.
A static IP address, also called a dedicated IP address, doesn’t change. This means whenever you connect to the internet after disconnecting, you’ll get the same IP address. It usually costs extra to get a static IP address.
And while dynamic IP addresses generally offer greater privacy and security for the average user, static IP addresses can be useful for certain systems.
Static vs. Dynamic IP address: Which is better
When it comes to choosing between a static and dynamic IP address, the "better" option largely depends on your specific needs and circumstances.
- Static IP addresses are ideal for businesses or users who require consistent and reliable access to online services, such as web hosting, remote access, or email servers. They make it easier to manage DNS records and are essential for certain applications that need a constant address. However, since static IPs don’t change, they can be more vulnerable to tracking and hacking.
- Dynamic IP addresses are often better suited for residential users or those who prioritize privacy. These IPs are assigned temporarily by your ISP and change periodically, making it harder for outsiders to track your online activities. Dynamic IPs are also generally less expensive and simpler for users who don’t need a consistent address.
- ExpressVPN’s dedicated IP feature offers a consistent IP address, which is useful if you need reliable access to certain networks, like corporate systems. Unlike traditional static IPs, ExpressVPN’s dedicated IPs come with the privacy benefits of a VPN, ensuring your activity remains protected. This option combines the stability of a static IP with enhanced security and privacy.
No matter your IP setup, ExpressVPN dynamic IPs or dedicated IP feature provide extra layers of privacy and protection, helping you stay secure whether you’re streaming, working, or browsing.
Why you may want a static IP address
Most residential internet services use a dynamic IP configuration through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). While a static IP address could be the best approach in some cases, it’s important that you know what they are good for, and see if you’re in one of these use cases. Here are the most common ones:
You want to host a server
For hosting game, web, email, or other types of servers, a static IP provides a consistent address for users to connect to, making connections easy.
Your IoT device requires it
Some Internet of Things (IoT) devices require static IPs to function correctly and remain consistently accessible for monitoring and control.
You want a more stable connection
File downloads and uploads tend to be slightly faster with a static IP.
You want more security
Static IPs facilitate the implementation of security measures like IP whitelisting, ensuring only authorized devices can access certain online services.
You want to simplify your network managementAssigning static IPs to devices makes network management easier, allowing for straightforward identification, troubleshooting, and configuration of networked devices.
How to set up a static IP address
Setting up a static IP address is fairly simple but varies per device. However, the first thing you should sort out before configuring is the static IP address itself. You would inquire with your internet service provider (ISP) about getting a static IP, which usually involves a small extra charge.
How to set a static IP address on a router
You can assign a static IP address through your router for any device on its network. To do this, you’ll need the MAC address of whatever device you want to configure with a static IP address, and that device must be connected to the router. Lastly, note that most routers have different software, so these are general instructions to get you started.
- Access the router. Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address into the address bar. You can usually find this on the back of your router or in the manual.
- Log in. Enter your username and password to log into the router’s admin panel. If you haven’t changed these from the defaults, they should also be on the router or manual.
- Navigate to LAN settings. Look for a section in the admin panel labeled “LAN” or “Network Settings”. This might be under “Advanced Settings” depending on your router.
- Find DHCP or static IP settings. Locate the DHCP settings within the LAN or Network Settings. You may need to switch from DHCP to Manual or Static IP configuration.
- Fill in the IP address, Gateway, Network prefix length, and DNS fields.
- Save and apply. After entering all necessary information, save and apply your changes. The router may need to restart for changes to take effect.
How to set a static IP address on Windows 10
Assigning a static IP to your Windows 10 device is much easier than on your router. Just follow these instructions:
- Go to Settings. Press the Windows key, type “Settings,” and press Enter.
- Click Network and Internet and then Network and Sharing Center.
- Click Change adapter settings on the left pane.
- Right-click your network connection and select Properties.
- Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click on Properties.
- Fill in the IP address, Gateway, Network prefix length, and DNS fields.
- Click OK to save your changes, then click OK again to exit the properties menu.
How to set a static IP address on Windows 11
The steps for Windows 11 are very similar to those on Windows 10:
- Open Settings. Click on the Start menu, select Settings, or press Windows + I on your keyboard.
- In the Settings menu, click on Network & Internet.
- Choose the network you are connected to. If you are using Wi-Fi, click on “Wi-Fi” and then select your network. For a wired connection, click on “Ethernet” and then on your network connection.
- Edit IP Assignment. Scroll down and click on “Hardware properties.” Then, find the “IP assignment” section and click the “Edit” button.
- Change to Manual. In the “Edit IP settings” window, change the setting from “Automatic (DHCP)” to “Manual.” Toggle on the “IPv4” switch to enable manual IP configuration.
- Fill in the IP address, Gateway, Network prefix length, and DNS fields.
- Click Save to apply your settings.
How to set a static IP address on macOS
To configure a static IP on your Mac, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Apple menu in the top left corner of your screen and select System Preferences.
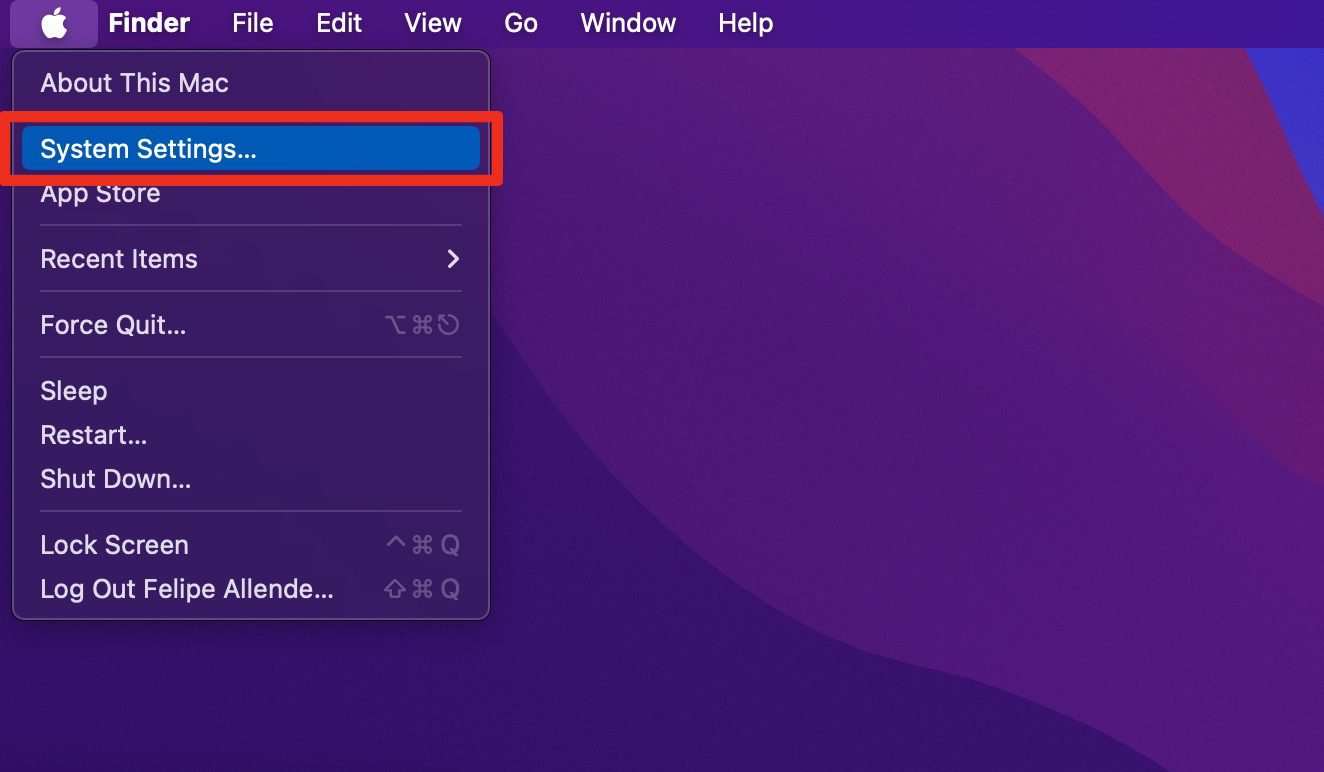
2. In the System Preferences window, find and click on Network.
3. Select the network connection you wish to configure from the list on the left side. This could be either Wi-Fi or Ethernet, depending on how your Mac is connected to the network.
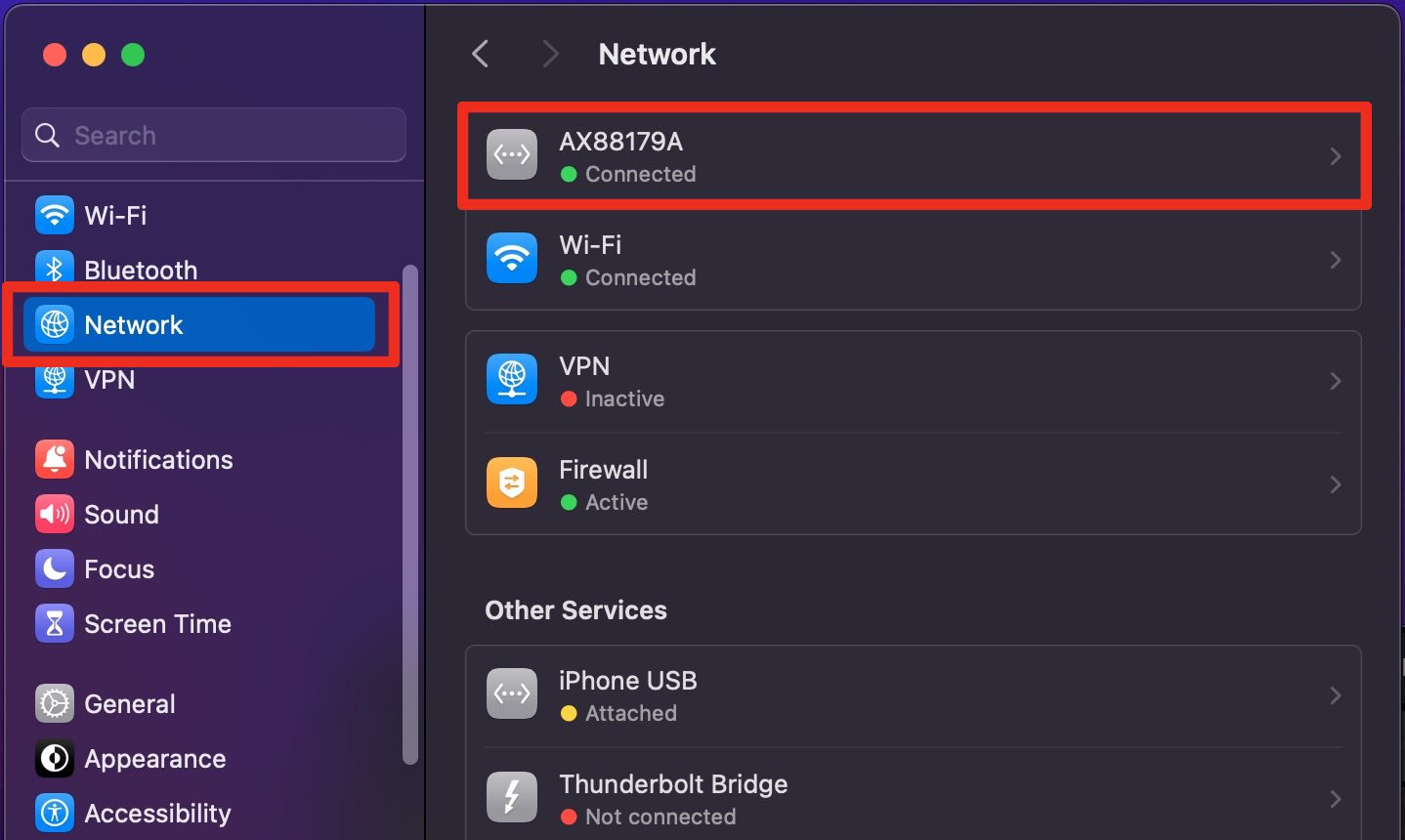
4. With the network selected, click on the Details button in the top right corner of the window.
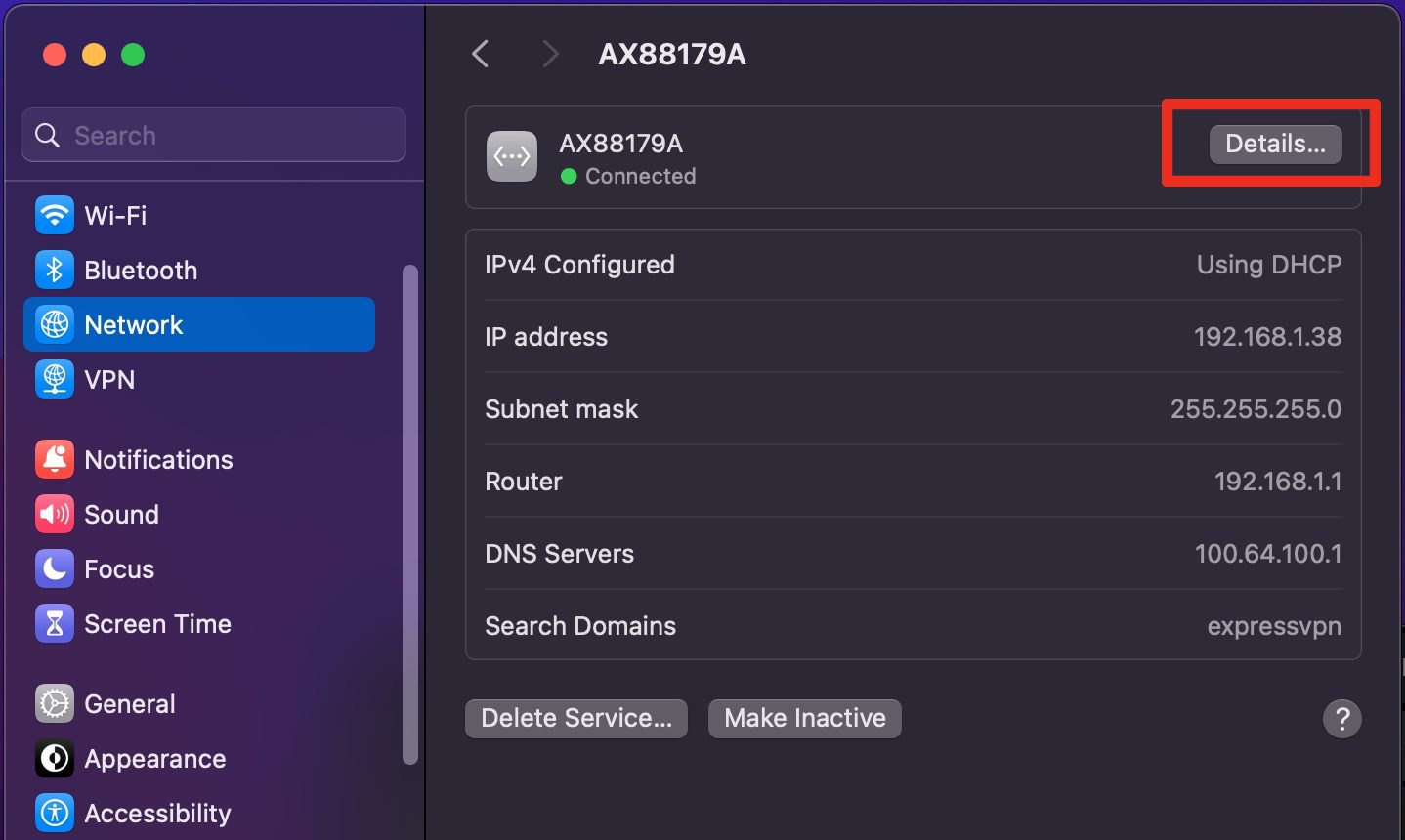
5. Click on the TCP/IP tab on the left.
6. Click on the dropdown menu next to "Configure IPv4" and select Manually from the list of options.
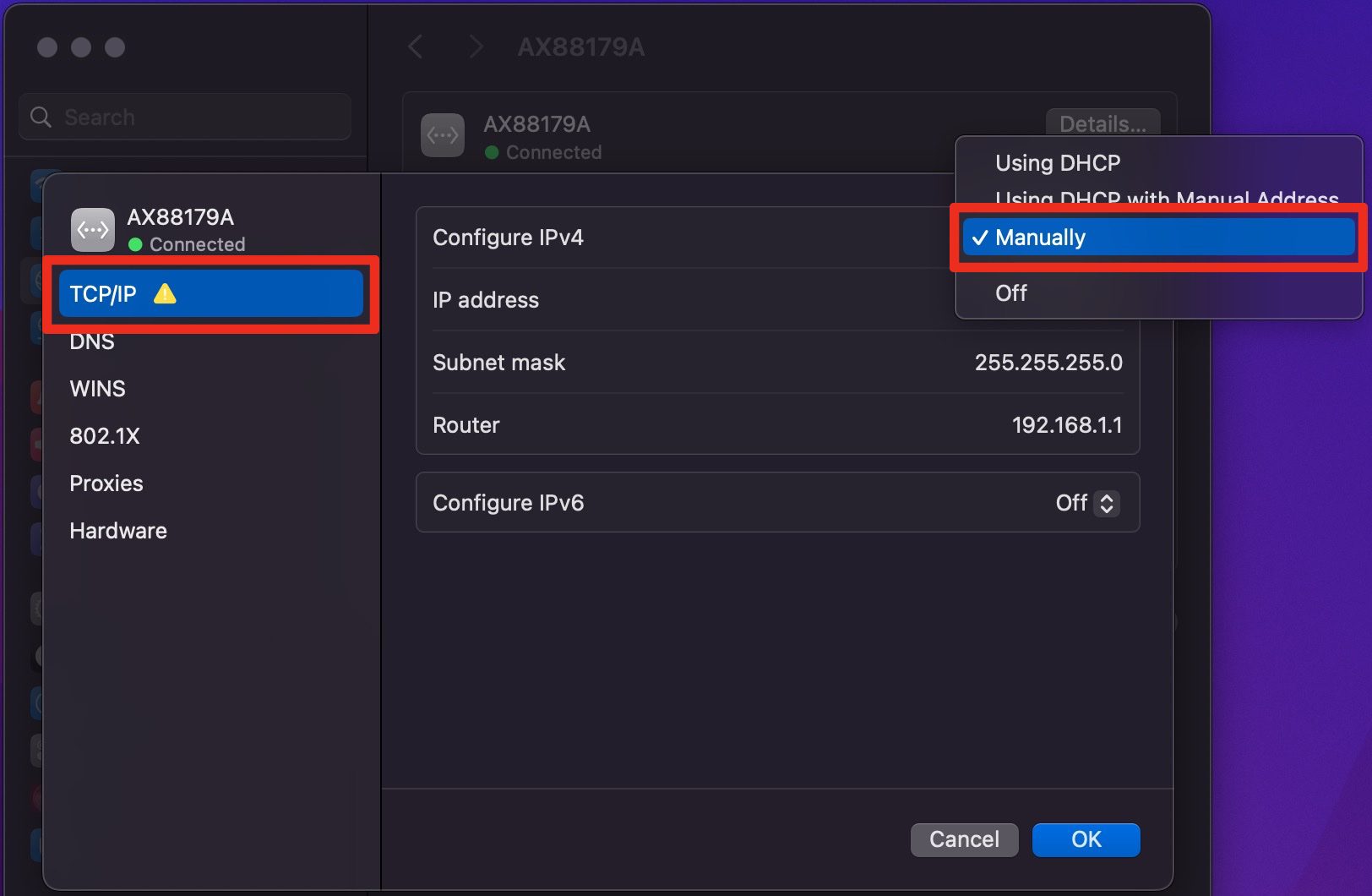
7. Fill in the IPv4 Address field with the static IP address you want to assign to your Mac.
8. Optionally, navigate to the DNS tab in the same window to manually enter DNS server addresses if required.
9. Click OK to close the Details settings window.
How to set a static IP address on Android
Setting up a static IP address on Android is straightforward. Just follow these steps:
- Tap on the Settings icon on your home screen or app drawer.
- Scroll down and tap on Wi-Fi. Ensure Wi-Fi is turned on, and you're connected to the network you want to configure.
- Select the gear icon beside your current network.
- Find the IP settings section and change it from DHCP to Static.
- Fill in the IP address, Gateway, Network prefix length, and DNS fields.
- Scroll down and tap Save to apply your new static IP settings.
How to set a static IP address on iOS
On iOS, the process is quite similar. Follow these instructions:
1. Tap the Settings icon on your home screen or App Library.

2. Next to the Wi-Fi network you're connected to, tap the i icon to access the network's settings.
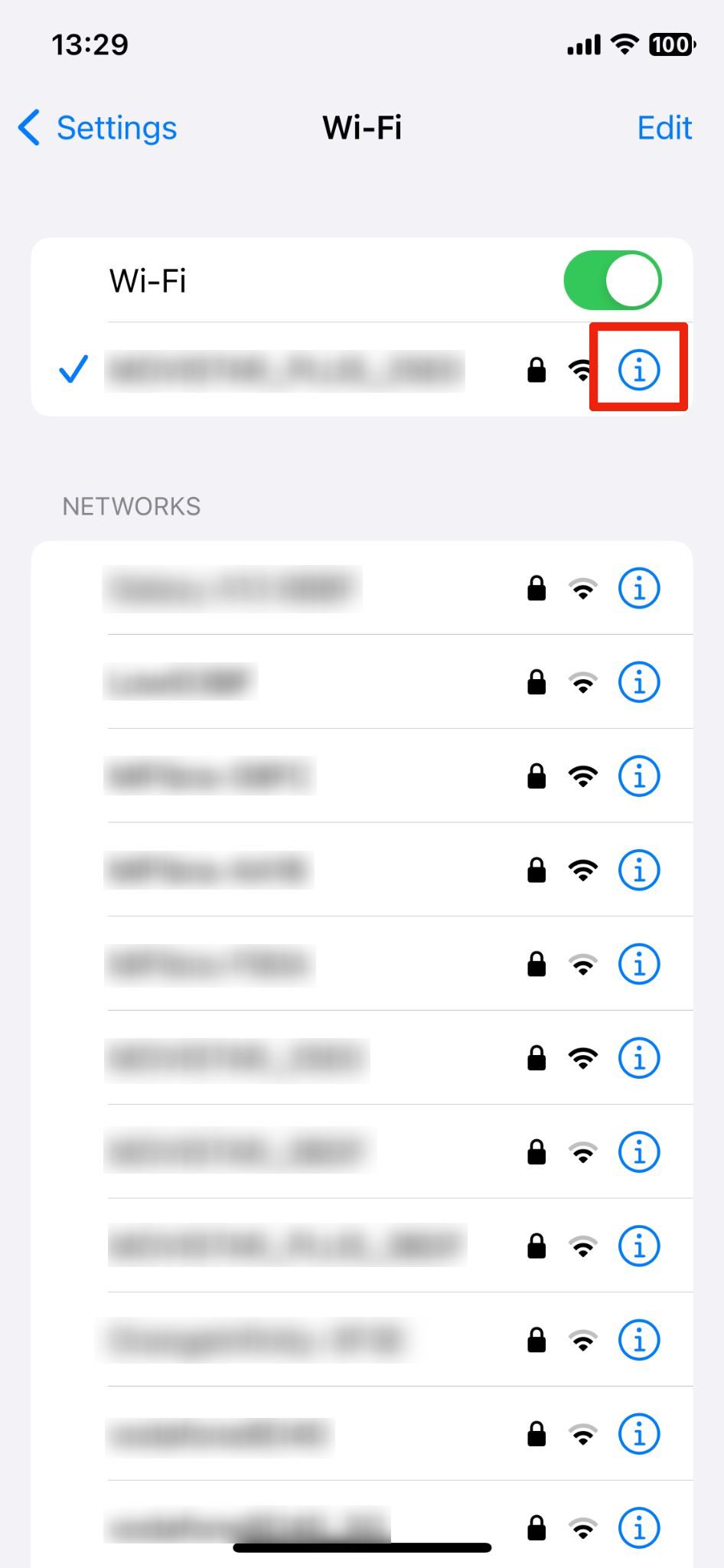
3. Scroll down and tap on Configure IP to change how your device acquires an IP address.
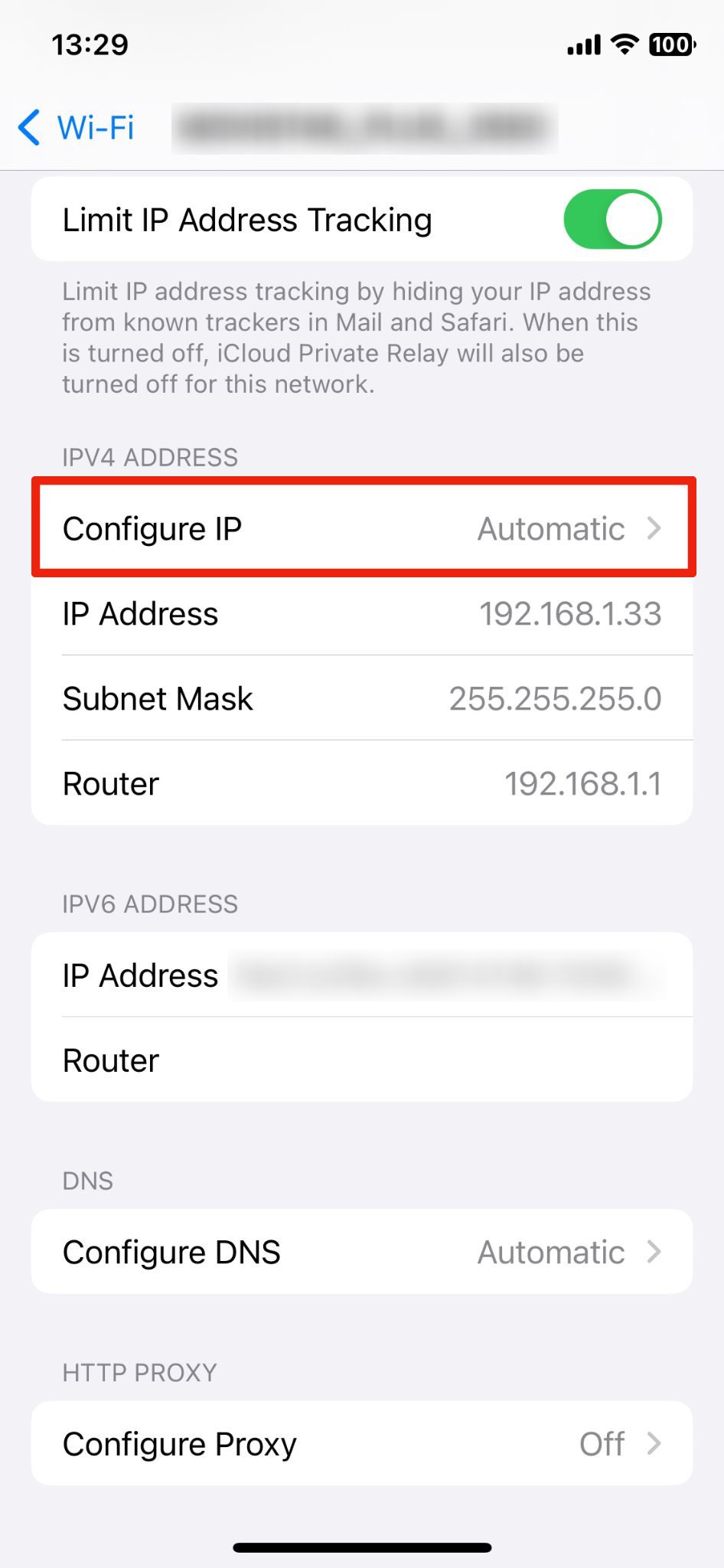
4. Tap Manual to switch from automatic (DHCP) to manual IP settings.
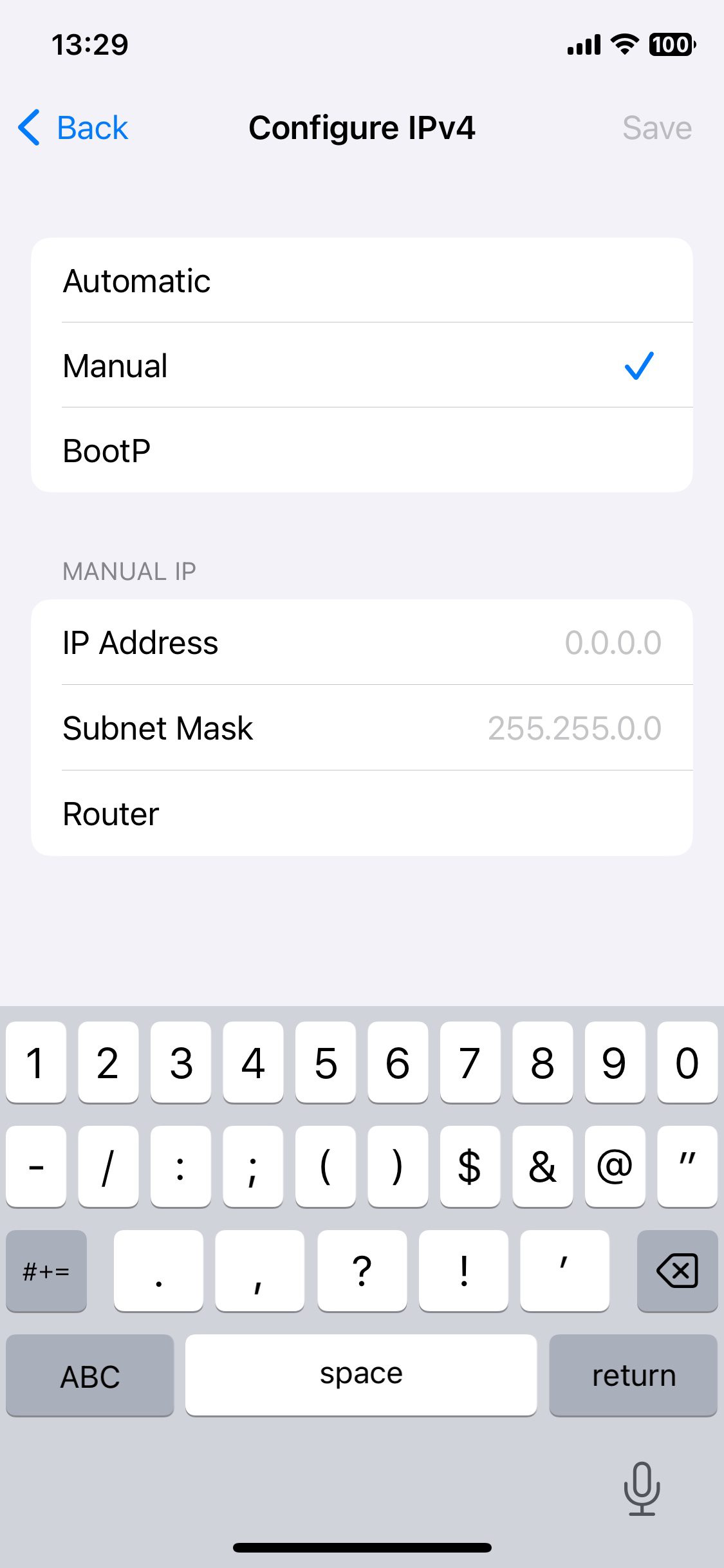
5. Fill in the IP address, Gateway, Network prefix length, and DNS fields.
6. Tap Save in the upper right corner to apply your changes.
How to set a static IP address on Linux
The process for Linux is a little more involved. Bear in mind that while you could do it by running a ip adr command, that change would be reversed with every reboot. To set up the static IP permanently, follow these steps:
- Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the terminal on your Linux desktop.
- Use the command ip addr or ifconfig to identify your network interface.
- Navigate to Netplan Configuration. Files are typically located in /etc/netplan/. Use ls /etc/netplan/ to list the configuration files.
- Use a text editor like nano or vim to edit the YAML configuration file found in the previous step.
- Modify the file to include your static IP settings under the appropriate network interface.
- Save the file and apply the changes by running sudo netplan apply.
How to set a static IP address on Raspberry Pi
Like with Linux, the process with Raspberry Pi is more involved than with other platforms. To configure the static IP, follow these steps:
- Access the terminal directly or via SSH if you’re remotely connected to your Raspberry Pi.
- Type sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf to edit the DHCP client configuration file with nano editor. You can replace nano with your preferred text editor.
- Scroll to the end of the file and add your static IP configuration.
- Press Ctrl + O to save the changes, then Ctrl + X to exit nano.
- To apply the changes, restart the DHCP client daemon with sudo service dhcpcd restart.
Does ExpressVPN offer static or dynamic IPs?
ExpressVPN does not offer traditional static IPs directly from an ISP. Instead, we primarily provide dynamic IPs, which change each time you connect to enhance your privacy. Each dynamic IP is shared among multiple users, making it harder for websites and apps to track individual activity and boosting anonymity.
For users who need a consistent IP address, ExpressVPN also offers a dedicated IP feature. This dedicated IP remains the same each time you connect but still includes the privacy benefits of a VPN, as it’s unique to you and cannot be traced back to your device by ExpressVPN.
Need a unique IP address? Try ExpressVPN’s dedicated IP feature
If you need consistent access to specific networks—like corporate systems—ExpressVPN now offers dedicated IPs in 29 global locations. Enjoy the flexibility of a unique IP address while keeping the privacy benefits of a secure VPN connection. Add the dedicated IP feature to your ExpressVPN subscription to make remote access smoother and more reliable.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN













Comments
I am with ExpressVPN for 7 years now, is the most expensive Vpn in the market but they provide good service for the price, you can't find faster Vpn without dropping speed for streaming or your sensitiv business in other countries, I purchased Aircove Wich is express vpn router and I have all my devices connected with no issues and I have so many other future beside Vpn like ad blockers and parental control and password management, the only thing I will say about the negative side is I feel recently customer service is not responding as fast as before, anyways I recommend this Vpn all the way, what you waiting for? Come and see it yourself